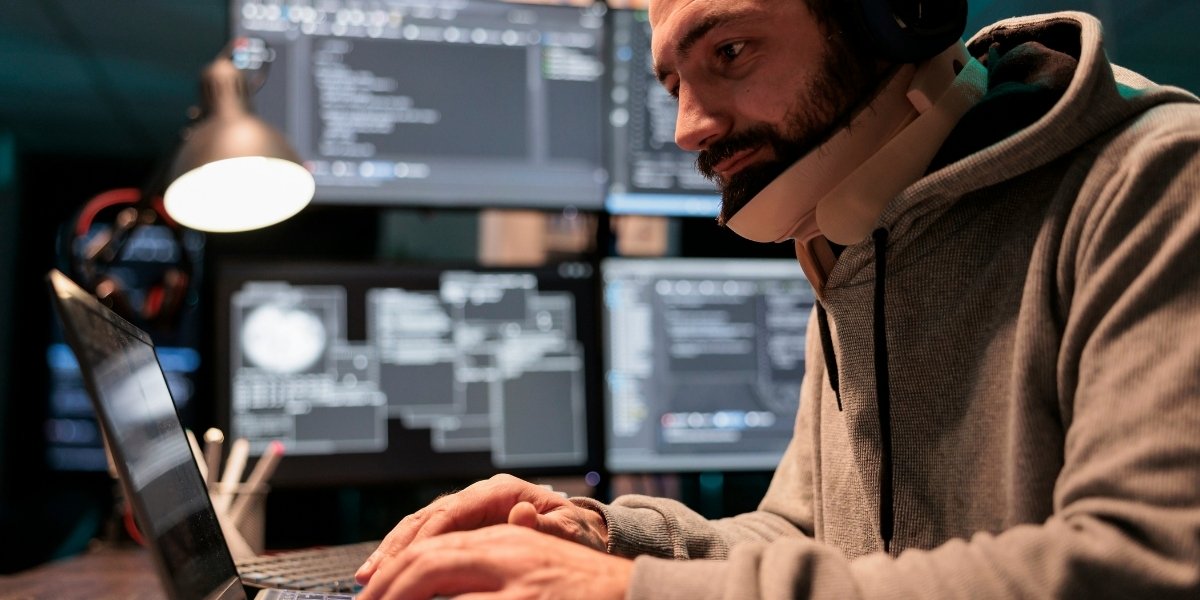
Ergonomics for Repetitive Task Workers: How to Stay Healthy and Productive
Workers who engage in repetitive tasks, whether in manufacturing, office environments, or service industries, are particularly vulnerable to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). These injuries, caused by repetitive motions, awkward postures, and extended periods of strain, can severely impact productivity and overall well-being. Fortunately, proper ergonomics can help reduce the risk of these injuries.
Read Also: The Role of Emotional Regulation in Mental Health
This article explores how workers involved in repetitive tasks can improve their posture, work setup, and daily habits to prevent strain and discomfort. Let’s dive into how ergonomic principles can benefit those performing repetitive actions and enhance their quality of life.
What Are Repetitive Tasks and Why Are They Problematic?
Repetitive tasks involve performing the same motions repeatedly over long periods. These tasks are common in various fields, from office work, where workers use keyboards and mice for extended periods, to industrial settings, where assembly lines require repetitive hand movements.
The challenge with these tasks lies in the physical strain they put on the body. Over time, this strain can lead to conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, and chronic back pain. The repeated nature of these actions often causes wear on joints, muscles, and nerves, which can result in long-term health issues if not addressed properly.
How Can Ergonomics Help Workers Performing Repetitive Tasks?
Ergonomics, the study of designing a workspace or task to fit the worker’s needs, is key to preventing injuries caused by repetitive tasks. By incorporating ergonomic principles, workers can significantly reduce strain and discomfort. Here are some core ergonomic strategies:
1. Proper Posture is Key
Maintaining a neutral posture is one of the most important ergonomic practices. Workers should ensure their body is aligned and their joints remain in a neutral position to avoid unnecessary stress. For instance, when sitting at a desk, feet should rest flat on the floor, knees should be at a 90-degree angle, and elbows should be close to the body at a comfortable angle to avoid strain.
2. Adjust Workstation Setup
The workstation should be tailored to the needs of the individual performing repetitive tasks. This can be achieved through adjustable chairs, desks, and work tools. The screen should be at eye level to prevent neck strain, and the keyboard and mouse should be positioned to allow for a relaxed arm posture.
3. Take Regular Breaks
Repetitive tasks can cause fatigue and strain, even if the proper posture is maintained. Workers should take regular breaks to give their muscles a chance to relax and recover. Research suggests that a 5–10 minute break every hour can reduce the risk of strain from repetitive motions.
4. Use Ergonomically Designed Tools and Equipment
For workers in manufacturing or industrial environments, using tools that are designed with ergonomics in mind can greatly reduce strain. For instance, power tools with cushioned handles and tools that require less force to operate can reduce stress on the hands and wrists.
Common Injuries from Repetitive Tasks and How to Prevent Them
Workers performing repetitive tasks are at risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), which include a variety of injuries to the muscles, nerves, and tendons. Some of the most common injuries include:
1. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This condition occurs when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed due to repetitive movements. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand.
Prevention Tip: Keep wrists straight while typing or using tools and take regular breaks to stretch and relieve pressure on the wrists.
2. Tendonitis
Tendonitis is the inflammation of a tendon caused by repetitive motion. It typically affects the shoulder, elbow, or wrist. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Prevention Tip: Avoid overuse of specific muscle groups by alternating tasks and using ergonomic tools that reduce strain.
3. Back Pain
Chronic back pain is a common complaint among workers who spend long hours sitting or standing in awkward postures. It can result from improper seating or standing positions and prolonged static positions.
Prevention Tip: Ensure that workstations are set up with proper lumbar support and that workers alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day.
The Role of Employers in Promoting Ergonomics for Repetitive Task Workers
While workers can take steps to improve their own ergonomics, employers play a crucial role in fostering a safe work environment. Employers should:
1. Provide Ergonomic Training
Workers should be trained on the importance of ergonomic practices and how to implement them in their daily tasks. Regular workshops or online training can help reinforce good habits and improve awareness.
2. Invest in Ergonomic Equipment
Employers should invest in ergonomic chairs, desks, and tools to ensure that workers have the right equipment to do their jobs safely. The initial cost of ergonomic tools may seem high, but the long-term benefits in terms of fewer injuries and higher productivity make it a worthwhile investment.
3. Encourage Breaks and Movement
Encouraging workers to take short breaks and engage in light physical activity can reduce the impact of repetitive tasks. Providing a designated area for stretching or relaxation during breaks can help workers recover from physical strain.
Can Ergonomics Reduce the Risk of Long-Term Injury?
The short answer is yes. Ergonomics is crucial in preventing long-term damage to workers’ health. By integrating ergonomic practices into daily routines, workers can minimize the physical strain that comes with repetitive tasks. Over time, these changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic pain or injuries, thus improving the worker’s overall well-being and productivity.
Read Also: Handwashing Techniques for Germ Prevention: Your Guide to Staying Healthy
Embracing Ergonomics for a Healthier Work Environment
Ergonomics for repetitive task workers isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. By incorporating ergonomic principles into their work routine, employees can protect themselves from debilitating injuries while boosting their efficiency and comfort. Whether in an office setting or an industrial workspace, implementing ergonomic practices should be a priority for both workers and employers alike. The result is a healthier, more productive workforce and a safer, more comfortable working environment.